Physical Vascular Therapy in Practice: Scientific Evidence and Therapeutic Applications
This page provides a collection of peer-reviewed studies and publications related to Bio-Electro-Magnetic Energy Regulation (BEMER) therapy. The research highlights the potential effects of BEMER on various health conditions, from chronic pain and fatigue to microcirculation and athletic performance. Each entry includes the study’s title, authors, publication details, and a brief summary of its findings.
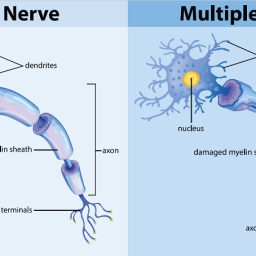
The Effect of Bio-Electromagnetic Energy Regulation Therapy on Erectile Dysfunction in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Triple-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
- Authors: Abdulaziz Ali Y Alzharani, Ali M Alshami, Turki Abualait, Hatem Al Azman, Foziah Jabbar Alshamrani, Yahya Hilal Alzahrani, Youssef A Althobaiti
- Publication Info: PMID: 39685520 | PMCID: PMC11642583 | DOI: 10.3390/jcm13237060
- Published: 2024
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39685520/
BEMER therapy improved erectile function and reduced fatigue in men with Multiple Sclerosis. Despite some risk factors, results were positive. Doctors and patients rarely discuss sexual health, which should change.
The effect of electro-magnetic-energy-regulation therapy on subjective sleep among elite players in Norwegian women’s football
- Authors: Moen, Frode, Svein Arne Pettersen, and Ellen F. Mosleth. 2024
- Publication Info: PMID: 39149571 | DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1343841
- Published: 2024
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39149571/
BEMER therapy improved the quality and duration of sleep in Norwegian elite footballers, especially on and after match nights. Before the therapy, post-match sleep was poor, which also affected recovery. After BEMER therapy, sleep improved significantly, the players reported better recovery and were very appreciative of the overall benefits. Focuses on subjective sleep — how the players felt about their sleep (quality and duration), based on self-reported daily sleep diaries. It compares periods with and without BEMER therapy over 273 days.
Effect of osteopathic manipulative treatment and Bio-Electro-Magnetic Energy Regulation (BEMER) therapy on generalized musculoskeletal neck pain in adults.
- Authors: Genevieve M Palmer, Nicholas Dominick, Melissa Kane, Sawyer Bawek, Blake Burch, Taylor Sanders, Davong Phrathep, Nicole Myers, Santiago Lorenzo
- Publication Info: PMID: 38033194 | DOI: 10.1515/jom-2023-0128 | ClinicalTrials.gov under the identifier NCT05889039
- Published: 2024
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38033194/
This study looked at how well Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment and BEMER therapies help adults with neck pain. BEMER therapy worked better than Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment or no treatment, and people felt less pain and more able to do daily activities. Using both treatments together showed a synergistic effect, leading to even greater improvement.
Treatment of patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) with an electromagnetic field coupled to biorhythmically defined impulse configuration: the MicrocircMODS study.
- Authors: Karl Werdan, Sebastian Nuding, Diethelm Kühnert, Ramzi Kolthoum, Artjom Schott, Felix Quitter, Andreas Wienke, Daniel Sedding Clin Res Cardiol.
- Publication Info: PMID: 37717230 | DOI: 10.1007/s00392-023-02293-2
- Published: 2024
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37717230/
This pilot study tested if Physical Vascular Therapy BEMER® (PVT) is safe and possible for patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), along with their regular treatment. The results showed a 25% improvement in blood flow and better overall heart function, including less need for medications that affect blood pressure. Physical Vascular Therapy was found to be safe, with no adverse events related to the treatment.
The Effects of “Physical BEMER® Vascular Therapy” on Work Performed During Repeated Wingate Sprints
- Authors: Collin M Fehr, Gary McEwen, Clay Robinson
- Publication Info: Res Q Exerc Sport. 2023 Sep;94(3):732-737. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2022.2053040. Epub 2022 Apr 28.
- Published: 2023
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35481952/
This study tested three recovery methods after intense exercise: BEMER therapy, active recovery and passive recovery (lying down). All methods led to similar performance results, BEMER therapy helps recovery by improving circulation, which leads to faster muscle repair, reduces soreness and improves sleep.
The effect of bio-electro-magnetic-energy-regulation therapy on sleep duration and sleep quality among elite players in Norwegian women’s football
- Authors: Frode Moen, Svein Arne Pettersen, Kine Gjertsås, Marte Vatn, Martijn Ravenhorst, Atle Kvålsvoll, Kristian Hovde Liland, Ellen F Mosleth
- Publication Info: Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 8:14:1230281. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1230281. eCollection 2023.
- Published: 2023
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37614490/
The study focuses on objective sleep — actual sleep data measured by sleep monitors and also looks at physical load on game daysGame-day stress worsened sleep, but 5 months of BEMER therapy improved sleep quality and duration. Players using BEMER over 440 hours saw the biggest benefits, based on sleep monitor data.
Study of the functional capacity and health status of patients with hip as well as knee osteoarthritis
- Authors: Anett Tóvári, Anikó Kőnigné Péter, Péter Tardi, Eleonóra Leidecker, Eszter Ambrus, Iuliana Boros-Balint, Mária Hermann, János Kránicz, Márta Hock
- Publication Info: Orv Hetil. 2022 Nov 27;163(48):1917-1922. Print 2022 Nov 27.
- Published: 2022
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36436060/
This study evaluated a 3-week complex conservative therapy for hip and knee osteoarthritis. Patients showed significant improvements in pain levels, daily functioning, overall health, and joint mobility. Overall, the therapy can be considered a promising option for managing osteoarthritis symptoms.
Physical Vascular Therapy (BEMER) Affects Heart Rate Asymmetry in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
- Authors: Zita Kreska, Péter Mátrai, Balázs Nemeth, Bella Ajtay, István Kiss, László Hejjel, Zénó Ajtay
- Publication Info: In Vivo. May-Jun 2022;36(3):1408-1415.
- Published: 2022
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35478109/
This study tested the short-term effects of BEMER Physical Vascular Therapy (PVT) on heart function in patients with heart disease. While standard heart rate measures showed no clear changes, PVT significantly improved heart rate asymmetry (HRA). This suggests HRA may be a better way to detect quick responses to Physical Vascular Therapy.
Effects of Acute Low-Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy on Aerobic Performance during a Preseason Training Camp: A Pilot Study
- Authors: Nauris Tamulevicius, Tanuj Wadhi, Guillermo R Oviedo, Ashmeet S Anand, Jung-Jung Tien, Fraser Houston, Eric Vlahov
- Publication Info: Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 20;18(14):7691. doi:10.3390/ijerph18147691.
- Published: 2021
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34300141/
This study tested BEMER therapy during preseason altitude training in endurance runners. The therapy showed some benefits in improving ventilatory threshold (VT). This suggests BEMER may help with endurance gains during short-term training.
Effects of osteopathic manipulative treatment and bio-electromagnetic energy regulation therapy on lower back pain
- Authors: Kyle Auger, Gregory Shedlock, Kasey Coutinho, Nicole E Myers, Santiago Lorenzo
- Publication Info: J Osteopath Med. 2021 Mar 2;121(6):561-569. doi: 10.1515/jom-2020-0132
- Published: 2021
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33694338/
This study looked at how osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), BEMER therapy, and both together help with long-term low back pain. Forty people were split into four groups and treated for three weeks. The group that got both OMT and BEMER had the biggest improvements in pain and quality of life.
Bio Electro Magnetic Energy Regulation (BEMER) therapy in myofascial pain dysfunction syndrome: A preliminary study.
- Authors: Kanaparthi A, Kesary SPR, Pujita C, Gopalaiah H. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020 Apr-Jun;10(2):38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Feb 3.
- Publication Info: PMID: 32090003
- Published: 2020
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32090003/
This study tested BEMER therapy as an added treatment for Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome (MPDS) is a chronic pain disorder. Forty patients were split into two groups—one received only medication, the other received medication plus BEMER therapy. The BEMER group showed better pain relief and improved mouth opening over two months. Combined therapy was more effective than medication alone.
Bio-Electro-Magnetic-Energy-Regulation (BEMER) for the treatment of type 1 complex regional pain syndrome: A Pilot study.
- Authors: Benedetti M., Cavazzuti L., Mosca M., Fusaro I. and Zati A.
- Publication Info: Physiotherapy Theory and Practice. 2020 Apr; 36(4):498-506. Epub 2018 Jul 9.
- Published: 2020
- PMID: 29985719
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29985719/
This study tested BEMER therapy for people with complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS-I). Thirty patients were split into two groups: one received real BEMER therapy with rehabilitation therapy, the other received sham BEMER with rehabilitation therapy. The BEMER group showed more pain relief and better limb function after 10 days and at 1-month follow-up. BEMER may be a helpful addition to rehab for CRPS-I.
BEMER Electromagnetic Field Therapy Reduces Cancer Cell Radioresistance by Enhanced ROS Formation and Induced DNA Damage.
- Authors: Storch K, Dickreuter E, Artati A, Adamski J, Cordes N.
- Publication Info: PLoS One. 2016 Dec 13;11(12):e0167931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167931. eCollection 2016.
- Published: 2016
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27959944/
This study explored the effects of low-dose electromagnetic fields (EMF) using BEMER therapy on cancer cells. BEMER treatment enhanced radiosensitization and increased DNA damage in cancer cells but did not improve sensitivity to chemotherapy or Cetuximab. The therapy caused significant changes in metabolic pathways but its effects on cancer treatment need further investigation.
BEMER Therapy Combined with Physiotherapy in Patients with Musculoskeletal Diseases: A Randomised, Controlled Double Blind Follow-Up Pilot Study.
- Authors: Gyulai F, Rába K, Baranyai I, Berkes E, Bender T.
- Publication Info: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:245742. doi: 10.1155/2015/245742. Epub 20.5.2015
- Published: 2020
- Link to original source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26078768
This study evaluated the effect of BEMER therapy in patients with chronic low back pain and knee osteoarthritis. In the short term, BEMER therapy reduced pain and fatigue in low back pain patients, while in knee osteoarthritis patients, long-term therapy showed benefits in reducing fatigue and improving vitality. The findings suggest BEMER may provide short-term relief for low back pain and long-term benefits for knee osteoarthritis.
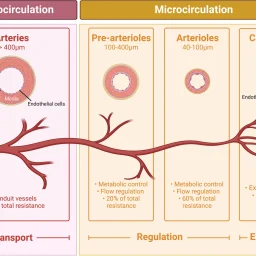
Effects of physical stimulation of spontaneous arteriolar vasomotion on microcirculation and the immune system in diabetes and impaired wound healing.
- Authors: Klopp R, Schulz J, Niemer W, Ruhnau KJ.
- Publication Info: Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2014 Jul;47(5):415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00391-013-0567-8. German.
- Published: 2014
- Link to original source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24271148
This study explored the impact of biorhythm-defined physical stimulation on microcirculation in older diabetes patients with impaired wound healing. Using advanced high-resolution methods, the treatment showed a complementary effect, enhancing therapeutic outcomes. The results suggest that the stimulation contributed to improved microcirculation and immune system functionality over 27 days.
The effects of the “physical BEMER® vascular therapy”, a method for the physical stimulation of the vasomotion of precapillary microvessels in case of impaired microcirculation, on sleep, pain and quality of life of patients with different clinical pictures on the basis of three scientifically validated scales.
- Authors: Bohn W, Hess L, Burger R.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl): S5-S12. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0037.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23940071/
This study evaluated the effects of BEMER® vascular therapy on sleep, pain, and quality of life in patients with various conditions. Results showed significant improvements in all areas surveyed after 6 weeks of treatment, regardless of the underlying disease.
Complementary-therapeutic stimulation of deficient autorhythmic arteriolar vasomotion by means of a biorhythmically physical stimulus on the microcirculation and the immune system in 50-year-old rehabilitation patients.
- Authors: Klopp RC, Niemer W, Schulz J.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl): S29-37. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0034.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24021604/
This study explored the effect of physical vasomotion stimulation on microcirculation and immune response in 50-year-old rehabilitation patients. Results indicated that the stimulation improved blood-flow regulation and immune response, enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Effects of physical stimulation of spontaneous arteriolar vasomotion in patients of various ages undergoing rehabilitation.
- Authors: Klopp RC, Niemer W, Schulz J.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl): S13-9. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0032.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24021602/
This study examined the effects of physical vasomotion stimulation on microcirculation in rehabilitation patients of different age groups. Results showed that older patients had greater microcirculatory improvements, but these effects faded faster compared to younger patients.
Influence of a specific, biorhythmically defined physical stimulus on deficient vasomotion in small-caliber arterioles in the subcutis in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy.
- Authors: Klopp RC, Niemer W, Schulz J, Ruhnau KJ.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl): S21-7. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0033.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24021603/
This study showed that biorhythmically defined physical vasomotion stimulation improved microcirculation and immune function in diabetic polyneuropathy patients with foot lesions. The treatment demonstrated complementary benefits alongside standard therapies over a 30-day period.
Effects of various physical treatment methods on arteriolar vasomotion and microhemodynamic functional characteristics in case of deficient regulation of organ blood flow. Results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study.
- Authors: Klopp RC, Niemer W, Schmidt W.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl): S39-46. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0035.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24021606/
In a placebo-controlled study, five out of six physical treatment devices were ineffective in improving blood-flow regulation, while one device using biorhythmically defined vasomotion stimulation showed therapeutic benefits.
The technological development history and current significance of the “physical BEMER® vascular therapy” in medicine.
- Authors: Bohn W.
- Publication Info: J Complement Integr Med. 2013;10(Suppl):S1-3. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2013-0036.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24021601/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems. (core study)
The BEMER® vascular therapy, developed in 1998, uses a specific signal configuration to improve microcirculatory characteristics through physical stimulation. Research has shown significant improvements in vasomotion, capillary blood distribution, and oxygen utilization, leading to the refinement of the signal for optimal therapeutic effects.
Effectiveness of pentoxifylline and of bio-electromagnetic therapy in lower limb obliterative arterial disease.
- Authors: Bernát SI. Orv Hetil.
- Publication Info: 2013 Oct 20;154(42):1674-9. doi: 10.1556/OH.2013.29693. Hungarian.
- Published: 2013
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24121220/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems
The study investigated the effects of bio-electromagnetic-regulation therapy and pentoxifylline on patients with peripheral arterial disease. Bio-electromagnetic therapy improved walking distance and pain-free period significantly, and when combined with pentoxifylline, the effects were even more pronounced. The combined therapy showed a high clinical effectiveness in 70% of patients.
Synergistic effect of EMF-BEMER-type pulsed weak electromagnetic field and HPMA-bound doxorubicin on mouse EL4 T-cell lymphoma.
- Authors: Říhová B, Etrych T, Šírová M, Tomala J, Ulbrich K, Kovář M., J Drug Target. 2011 Dec;19(10):890-9. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2011.622403. Epub 2011 Oct 10
- Publication Info: PMID: 21981636
- Published: 2011
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21981636/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems
The study tested the effects of BEMER-type electromagnetic fields (EMF) and doxorubicin on mouse T-cell lymphoma. EMF slowed tumor growth and increased survival, especially in weakened mice. Combining EMF with low doses of doxorubicin showed a stronger antitumor effect, offering a potential treatment for advanced cancer.
Long-term Effects of Bio-electromagnetic-energy regulation Therapy on Fatigue in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis.
- Authors: Ziemssen T, Piatkowski J, Haase R.
- Publication Info: Altern Ther Health Med. 2011 Nov-Dec;17(6):22-8.
- Published: 2011
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22314716/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems
This study examined the long-term effects of BEMER electromagnetic therapy on fatigue in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. After switching from placebo to treatment, patients showed significant reductions in fatigue, and benefits persisted for up to three years. BEMER therapy was well-tolerated and could be a useful treatment for MS-related fatigue.
Effect of BEMER magnetic field therapy on the level of fatigue in patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial.
- Authors: Piatkowski J, Kern S, Ziemssen T.
- Publication Info: J Altern Complement Med. 2009 May;15(5):507-11. doi: 10.1089/acm.2008.0501.
- Published: 2009
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19422286/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems
This randomized trial evaluated the effect of BEMER magnetic field therapy on fatigue in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. After 12 weeks, the treatment group showed significant improvements in fatigue levels, particularly in physical and cognitive fatigue.
Effects of weak, low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields (BEMER type) on gene expression of human mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes: an in vitro study.
- Authors: Walther M1, Mayer F, Kafka W, Schütze N.
- Publication Info: Electromagn Biol Med. 2007;26(3):179-90.
- Published: 2007
- Link to original source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17886005/
Note: This study used the BEMER 3000 Plus device, an earlier model with different signal parameters and features compared to newer BEMER systems
This study explored the effects of BEMER-type electromagnetic fields (BTEMF) on gene expression in human mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes. The results showed that BTEMF influenced genes related to cell metabolism and matrix structure, with no increase in cancer-related genes. These findings provide insights into the therapeutic potential of BTEMF in cell regeneration.
Important Notes and Resources
This summary is based on the current list of peer-reviewed studies on Bio-Electro-Magnetic Energy Regulation (BEMER) therapy available as of Spring 2025. New studies may have been released since this compilation. For the most accurate and updated information, please refer to the respective journal databases or PubMed.
Web Sources
- PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ – A free resource from the U.S. National Library of Medicine with access to millions of biomedical and life sciences articles.
- Frontiers: https://www.frontiersin.org/ – An open-access publisher known for peer-reviewed research across health, science, and technology.
- PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/ – A multidisciplinary open-access journal that publishes original research in all areas of science and medicine.
- Hindawi (Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine): https://www.hindawi.com/ – Publishes peer-reviewed journals across science, technology, and medicine with a strong focus on open-access research.
- De Gruyter: https://www.degruyter.com/ – An academic publisher offering journals in medicine and complementary therapies, including osteopathy and integrative medicine.
- Taylor & Francis Online: https://www.tandfonline.com/ – Publishes scholarly research journals, including those in sports science, rehabilitation, and physical health.
- MDPI (International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health): https://www.mdpi.com/ – A large open-access publisher covering public health, environmental sciences, and medical topics.
- Springer: https://link.springer.com/ – A major global publisher of scientific, technical, and medical research journals and books.
- Akadémiai Kiadó (Orvosi Hetilap): https://akjournals.com/ – Hungary’s leading academic publisher, offering peer-reviewed medical journals including Orvosi Hetilap.
Physical Vascular Therapy in Practice – Scientific Evidence and Therapeutic Applications